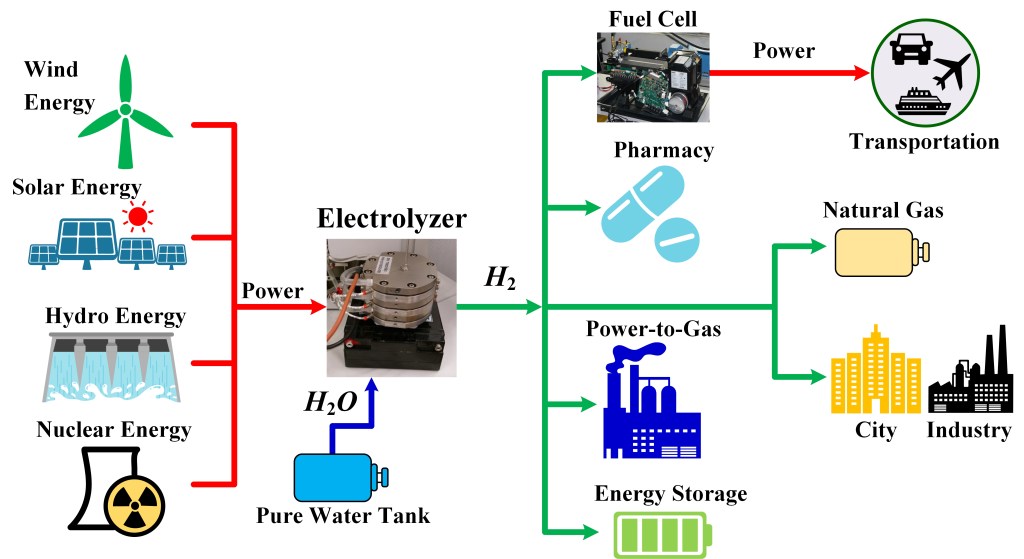
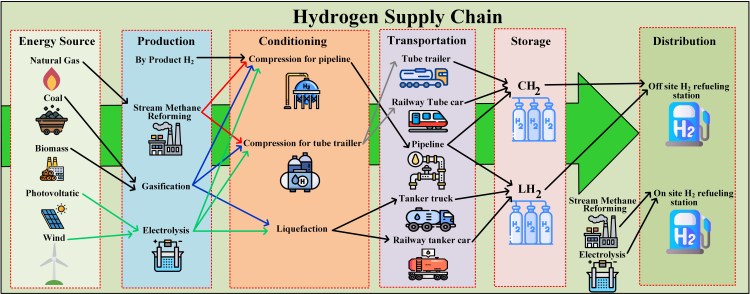
To decarbonize the industry and transportation sectors responsible for global warming, the use of hydrogen generated through the water electrolysis process coupled with renewable energy sources (RES) is an attractive and promising alternative.
Indeed, the hydrogen gas has a high energy mass density, and it can be recovered in various industrial applications (refineries, steel industry, production of ammonia and fertilizer, etc.) but also supply a fuel cell to produce electrical energy and if necessary thermal energy in cogeneration.
Moreover, the development plan presented by Nicolas Hulot encourages the production of “green” hydrogen by electrolysis of water to replace the steam reforming of CO2-emitting natural gas. Currently, the proton exchange membrane PEM electrolyzer technology is the most suitable for coupling to intermittent energy sources because it makes it possible to respond more quickly than the alkaline electrolyzer to sudden variations in power.
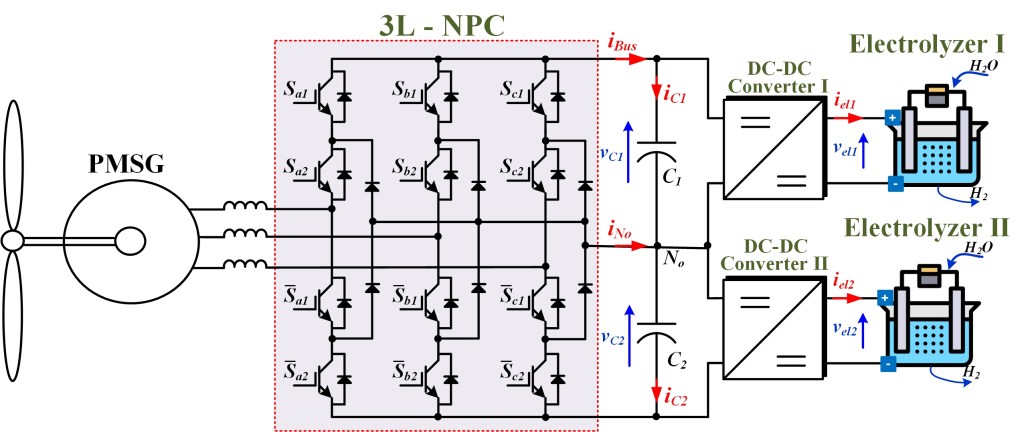
The power electronic conversion system is a challenging issue in the hydrogen production systems supplied by RES in terms of enhancing the efficiency of conversion energy to hydrogen. Because the behavior of RESs are strong intermittent characteristics and the DC voltage level is quite high (>100V). However, the PEM electrolyzer needs to supply a very low DC voltage (<10V).
The main issues of this topic are,
- The development of new topologies power converter with control algorithm for the PEM electrolyzer application.
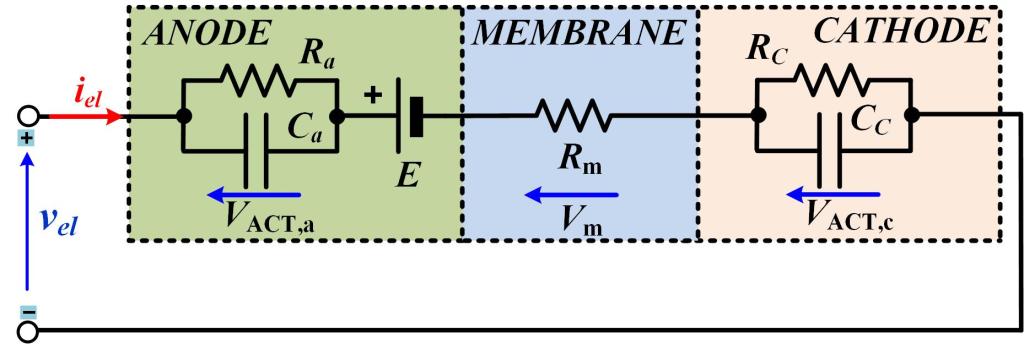
- The study PEM electrolyzer modeling (i.e., static, and dynamic model).
- Performance optimization of the hydrogen production system.
- The increase in lifespan by limiting degradation of PEM electrolyzer.







Electrical Engineering – Thai French Research Center